Tourniquet technique to reduce hemorrhage in placenta accreta to allow transportation of patient to tertiary care hospital.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29052/IJEHSR.v9.i4.2021.525-528Keywords:
Placenta Accreta, Cesarean Hysterectomy, Tourniquet, Hemorrhage.Abstract
Background: Placenta accreta is an obstetrical complication that can result in life-threatening hemorrhage if not managed adequately and cause high maternal morbidity. Cesarean hysterectomy is an effective method to control intra-operative bleeding.
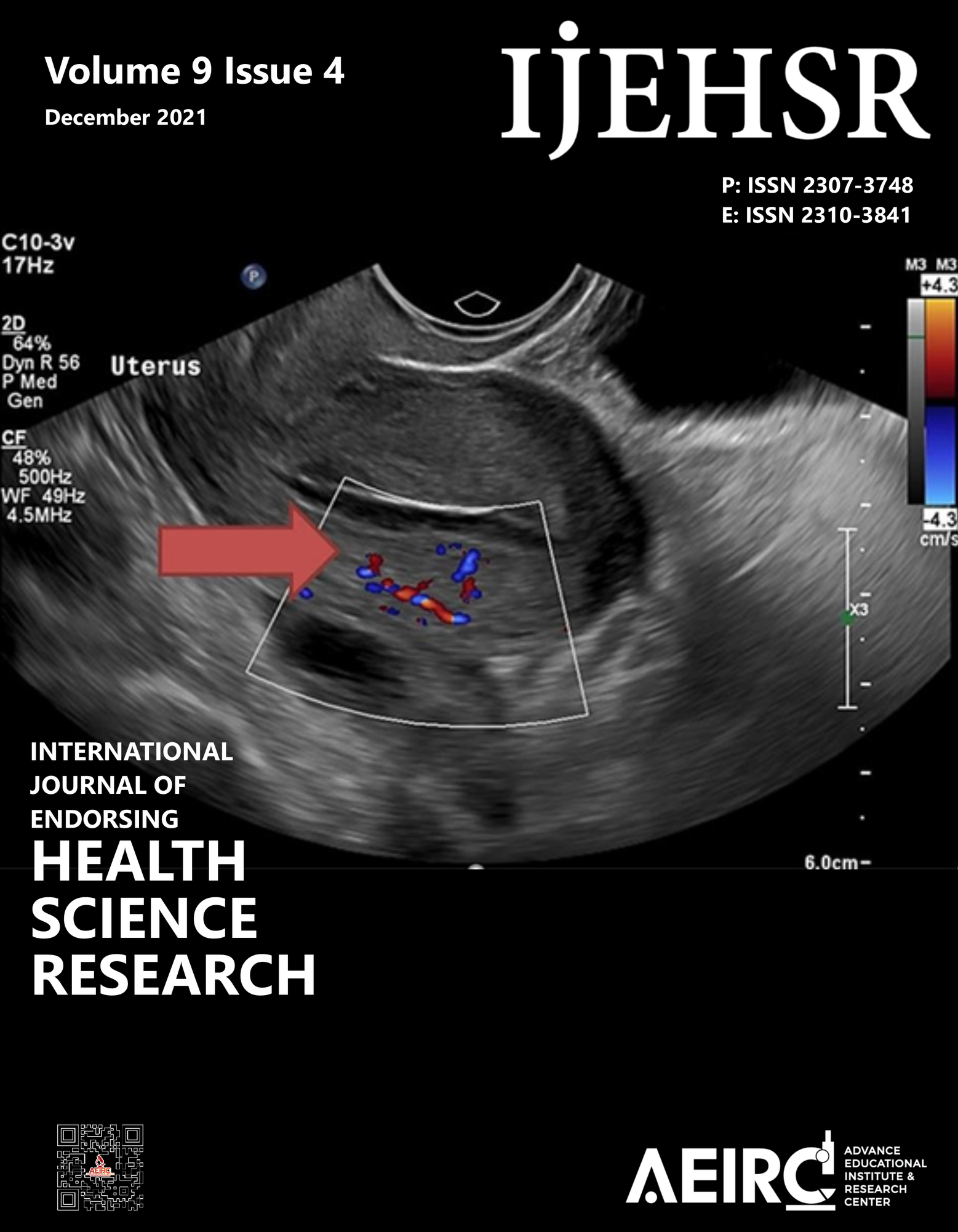
Case Presentation: We present a case of placenta accreta that was diagnosed intra-operatively in secondary care hospital. Due to the lack of a multidisciplinary team, bleeding was temporarily controlled by tying a tourniquet using a Foley catheter around the lower uterine segment with the tourniquet left in situ.
Management & Results: The patient was shifted to a tertiary care hospital. This novel tourniquet technique bought time to transport the patient, arrange for a multidisciplinary team needed for this patient's management, and reduce hemorrhage, which directly determined maternal outcome.
Conclusion: In this case report, we present that using a Foley catheter as a simple cervical tourniquet can effectively reduce hemorrhage, particularly in the case of blood loss originating from the placenta.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 The Author(s)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.